Understanding Prostate Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancer among men worldwide. Early detection and advancements in medical treatments have significantly improved outcomes for many patients. This blog will provide an overview of prostate cancer, its causes, symptoms, and available treatment options.
What is Prostate Cancer?
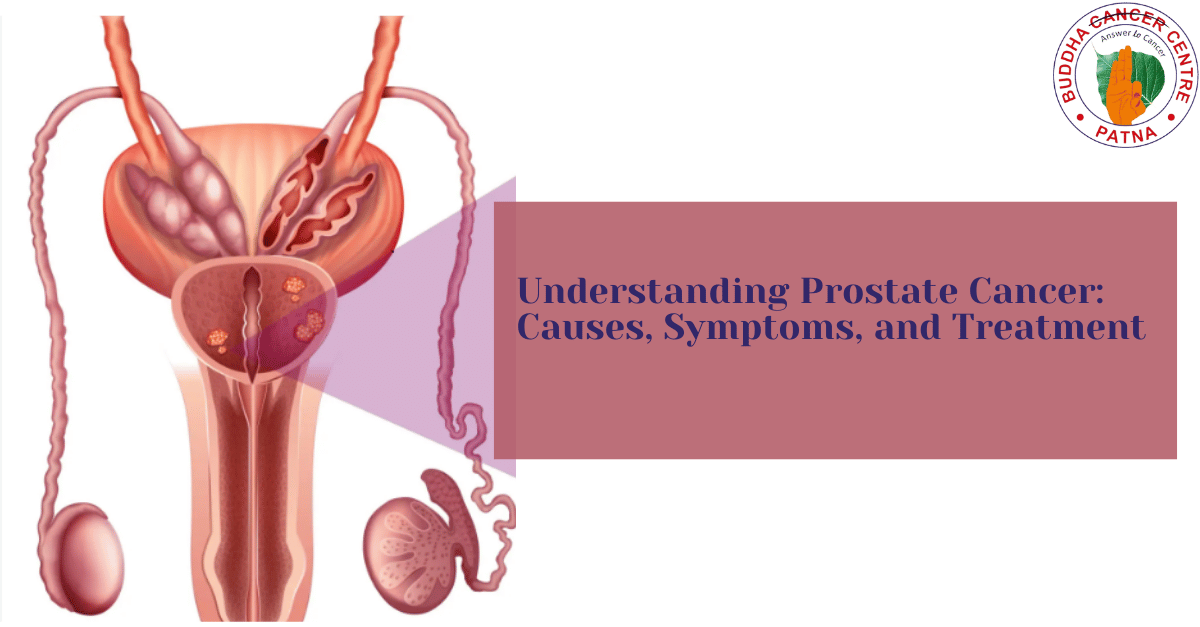
Prostate cancer is a type of cancer that develops in the prostate gland, a small, walnut-shaped organ in males that produces seminal fluid. This gland plays a crucial role in male reproductive health, and its location just below the bladder makes it a vital part of the urinary system.
Most prostate cancers grow slowly and may not cause significant harm during a man’s lifetime. However, some types are aggressive and can spread rapidly if left untreated, making early diagnosis critical.
Causes of Prostate Cancer
While the exact cause of prostate cancer is not fully understood, several factors have been linked to an increased risk of developing the disease:
- Age:The risk of prostate cancer increases significantly with age, especially after 50 years.
- Family History: A family history of prostate cancer or certain genetic mutations (e.g., BRCA1 and BRCA2) can raise the risk.
- Hormonal Factors: Elevated levels of testosterone and other androgens can contribute to the development and progression of prostate cancer.
- Lifestyle and Diet:Diets high in red meat, processed foods, and dairy, along with low fruit and vegetable consumption, have been associated with a higher risk. Obesity and sedentary lifestyles may also play a role.
Symptoms of Prostate Cancer
In its early stages, prostate cancer often presents no noticeable symptoms. However, as the disease progresses, the following signs may appear:
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Difficulty starting or stopping urination
- Weak or interrupted urinary stream
- Pain or burning sensation during urination
- Blood in urine or semen
- Erectile dysfunction
- Pain in the lower back, hips, or thighs (indicating possible spread to bones)
It is essential to note that these symptoms can also be caused by non-cancerous conditions like benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or prostatitis. Therefore, consulting a doctor for proper evaluation is critical.
Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer
1.Screening Tests
- Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test: Measures the level of PSA, a protein produced by the prostate, in the blood. Elevated levels can indicate cancer or other prostate conditions.
- Digital Rectal Exam (DRE): A doctor manually examines the prostate through the rectum to detect abnormalities.
- Consult Your Doctor: If you're experiencing side effects like nausea, work with your healthcare provider to create a tailored nutrition plan.
2.Diagnostic Procedures
Biopsy: A tissue sample is taken from the prostate and analyzed for cancerous cells.
Imaging Tests: MRI, CT scans, or bone scans may be used to assess the extent of cancer spread.
Treatment Options for Prostate Cancer
The treatment plan for prostate cancer depends on factors such as the stage of cancer, the patient’s overall health, and personal preferences. Here are the primary treatment approaches:
1.Active Surveillance or Watchful Waiting
- Suitable for slow-growing cancers. Regular monitoring through PSA tests and biopsies is conducted without immediate treatment.
2.Surgery
- Radical Prostatectomy: Removal of the prostate gland and surrounding tissues. This is often recommended for localized cancer.
3.Radiation Therapy
- High-energy rays are used to kill cancer cells. This can be external beam radiation or brachytherapy (internal radiation)
4.Hormone Therapy
- Reduces testosterone levels to slow the growth of cancer. This is often used for advanced or recurrent prostate cancer.
5.Chemotherapy
- Utilizes drugs to destroy rapidly growing cancer cells, particularly in cases where the cancer has spread beyond the prostate.
6.Targeted Therapy
- Focuses on specific genetic mutations or proteins that contribute to cancer growth.
7.Immunotherapy
- Enhances the body’s immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells.
Preventing Prostate Cancer
While prostate cancer cannot always be prevented, certain lifestyle changes may help reduce the risk:
- Maintain a healthy weight and engage in regular physical activity.
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Limit consumption of red meat and high-fat dairy products.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol intake.
- Discuss regular screening with your doctor, especially if you have a family history or other risk factors.
Prostate cancer, though common, is highly treatable when detected early. Understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms, and exploring treatment options empower men to take control of their health. Regular screenings and healthy lifestyle choices are key to minimizing risk and improving outcomes. If you have concerns about prostate cancer, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional.